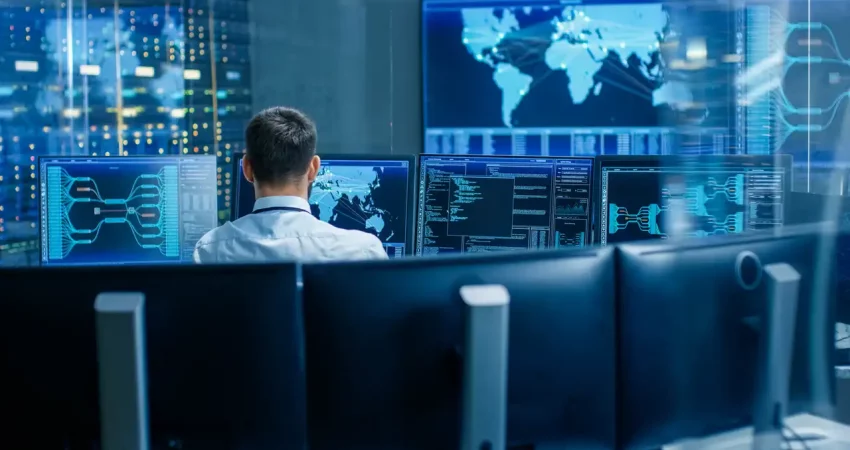
In an era where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, organizations are turning to automation as a vital strategy for transforming security operations management. The ability to automate security operations not only enhances efficiency but also significantly improves incident response times and overall security posture. This article explores how automation is reshaping security operations management, the benefits it offers, and the challenges organizations may face in its implementation.
Understanding Security Operations Management
Security operations management involves the processes and technologies used to monitor, detect, respond to, and recover from security incidents. This field encompasses various functions, including threat detection, incident response, compliance management, and risk assessment. Traditionally, these tasks have been labor-intensive, requiring significant human oversight and intervention. However, the rise of automation is changing the landscape, allowing organizations to streamline their security processes.
The Role of Automation in Security Operations
1. Enhanced Threat Detection
One of the primary benefits of automation in security operations is improved threat detection. Automated systems can analyze vast amounts of data in real time, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security threat. For example, machine learning algorithms can be trained to recognize unusual behavior in network traffic, flagging potential cyber threats before they escalate. By automating the threat detection process, organizations can respond more swiftly, minimizing the impact of security incidents.
2. Faster Incident Response
When a security incident occurs, time is of the essence. Automated security operations can significantly reduce the time it takes to respond to incidents. Automated incident response solutions can execute predefined playbooks, initiating immediate actions such as isolating affected systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, or notifying relevant personnel. This rapid response capability minimizes damage and helps organizations recover more quickly from security breaches.
3. Improved Efficiency and Resource Allocation
By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, security teams can focus on more strategic initiatives. For instance, routine tasks such as log analysis, vulnerability scanning, and compliance reporting can be automated, freeing up security professionals to concentrate on high-priority activities. This shift not only enhances efficiency but also optimizes resource allocation within the security team.
4. Consistent Compliance Management
Compliance with industry regulations and standards is a critical aspect of security operations management. Automation can help organizations ensure consistent compliance by automating reporting and documentation processes. Automated compliance tools can track regulatory requirements, generate real-time reports, and alert teams to potential compliance gaps. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of non-compliance and associated penalties.
5. Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
Automation facilitates better collaboration and communication among security teams. Automated tools can centralize information and streamline workflows, ensuring that all team members have access to the same data and insights. This transparency enhances coordination during incident response efforts, leading to more effective resolution of security incidents.
Benefits of Automating Security Operations
1. Cost Savings
While the initial investment in automation tools may be significant, the long-term cost savings can be substantial. By reducing the need for manual intervention and improving incident response times, organizations can lower the costs associated with security breaches and operational inefficiencies.
2. Increased Accuracy
Automated systems are less prone to human error, which can lead to more accurate threat detection and incident response. By minimizing the risk of oversight, organizations can enhance their overall security posture.
3. Scalability
As organizations grow, their security needs become more complex. Automation provides the scalability necessary to manage increased security demands without overwhelming existing resources. Automated systems can easily adapt to changing environments, making it easier for organizations to maintain effective security operations.
4. Improved Security Posture
By leveraging automation, organizations can enhance their overall security posture. Rapid threat detection and response capabilities, combined with consistent compliance management, contribute to a more resilient security framework. This proactive approach helps organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Challenges in Implementing Automation
1. Integration with Existing Systems
One of the primary challenges organizations face when implementing automation in security operations is integrating new tools with existing systems. Ensuring compatibility and seamless data flow between different solutions can be complex and time-consuming.
2. Skill Gaps and Training
Automation may require security professionals to develop new skills and competencies. Organizations need to invest in training and upskilling their teams to effectively leverage automated tools and technologies. Without proper training, the benefits of automation may not be fully realized.
3. Over-Reliance on Automation
While automation can enhance security operations, over-reliance on automated systems can lead to complacency. Organizations must strike a balance between automation and human oversight, ensuring that security teams remain engaged and proactive in their approach.
4. Data Privacy Concerns
Automating security operations often involves processing sensitive data. Organizations must ensure that their automated systems comply with data privacy regulations and maintain the confidentiality of sensitive information.
Best Practices for Automating Security Operations
1. Start Small and Scale Gradually
Organizations should begin by automating specific tasks or processes before scaling to a comprehensive automation strategy. Starting small allows teams to gain experience with automation tools and identify any potential challenges before full implementation.
2. Develop Clear Policies and Procedures
Establishing clear policies and procedures for automation is crucial. Organizations should define the scope of automation, establish protocols for incident response, and outline roles and responsibilities for security teams.
3. Foster a Culture of Continuous Improvement
Automation should be viewed as an ongoing process rather than a one-time solution. Organizations should regularly review and refine their automated processes to ensure they remain effective in addressing emerging threats.
4. Invest in Training and Development
Investing in training and development for security teams is essential for maximizing the benefits of automation. Organizations should provide opportunities for continuous learning to ensure that personnel are equipped to leverage automated tools effectively.
Conclusion
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the need for effective security operations management has never been more critical. By embracing automation, organizations can transform their security operations, enhancing threat detection, incident response, and overall efficiency. While challenges exist, implementing best practices for automation can help organizations navigate these complexities and ultimately strengthen their security posture. The future of security operations management lies in the ability to automate security operations, enabling organizations to stay one step ahead of potential threats.